Automate MFA Testing with Cypress — Tutorial, Code & Best Practices
TL;DR
To automate MFA testing with Cypress, use GetMyMFA's API to fetch SMS verification codes during your E2E test. Create a custom Cypress command that calls the /v1/{phoneId}/mfa/latest endpoint, extracts the mfaCode, and types it into the verification input using cy.get and cy.type.
Introduction & Context
If you are running end-to-end tests with Cypress and your application uses Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA), you have probably run into the same wall as everyone else: your automated tests stop at the MFA screen. Some teams disable MFA in their test environment (a risky shortcut), others go back to manual testing, and many simply skip testing MFA flows altogether.
None of these options are great. In this tutorial, we will walk through a clean, production-ready approach to automating SMS-based MFA with Cypress and the GetMyMFA API. By the end, you will have a working test that logs in, retrieves the MFA code programmatically, and completes authentication, all without touching a phone.
We previously covered this same workflow using Playwright. If you are using Cypress instead, this guide is for you. The same pattern can also be applied to other critical flows like financial transactions or sensitive approvals.
What we will build
A Cypress E2E test that handles the full SMS-based MFA login flow automatically. Here is what the test does:
- Opens the login page and enters credentials
- Waits for the MFA prompt to appear
- Calls the GetMyMFA API to retrieve the latest verification code
- Fills in the code and submits
- Verifies that the login succeeded
Complete source code is available for download at the end of this article.
Overview: How the flow works
Whether you use Cypress, Playwright, or any other framework, the high-level flow is the same. Here is how the pieces fit together:
- Start sign-in. Your Cypress test navigates to the login page and enters the user credentials.
- App sends SMS. The application sends an MFA code by SMS to a GetMyMFA virtual number.
- Code exposed via API. GetMyMFA captures the SMS and makes the code available through its API.
- Fetch the code. Your test calls the API using
cy.request()to get the latest code. - Submit the code. The test types the code into the MFA form and completes authentication.
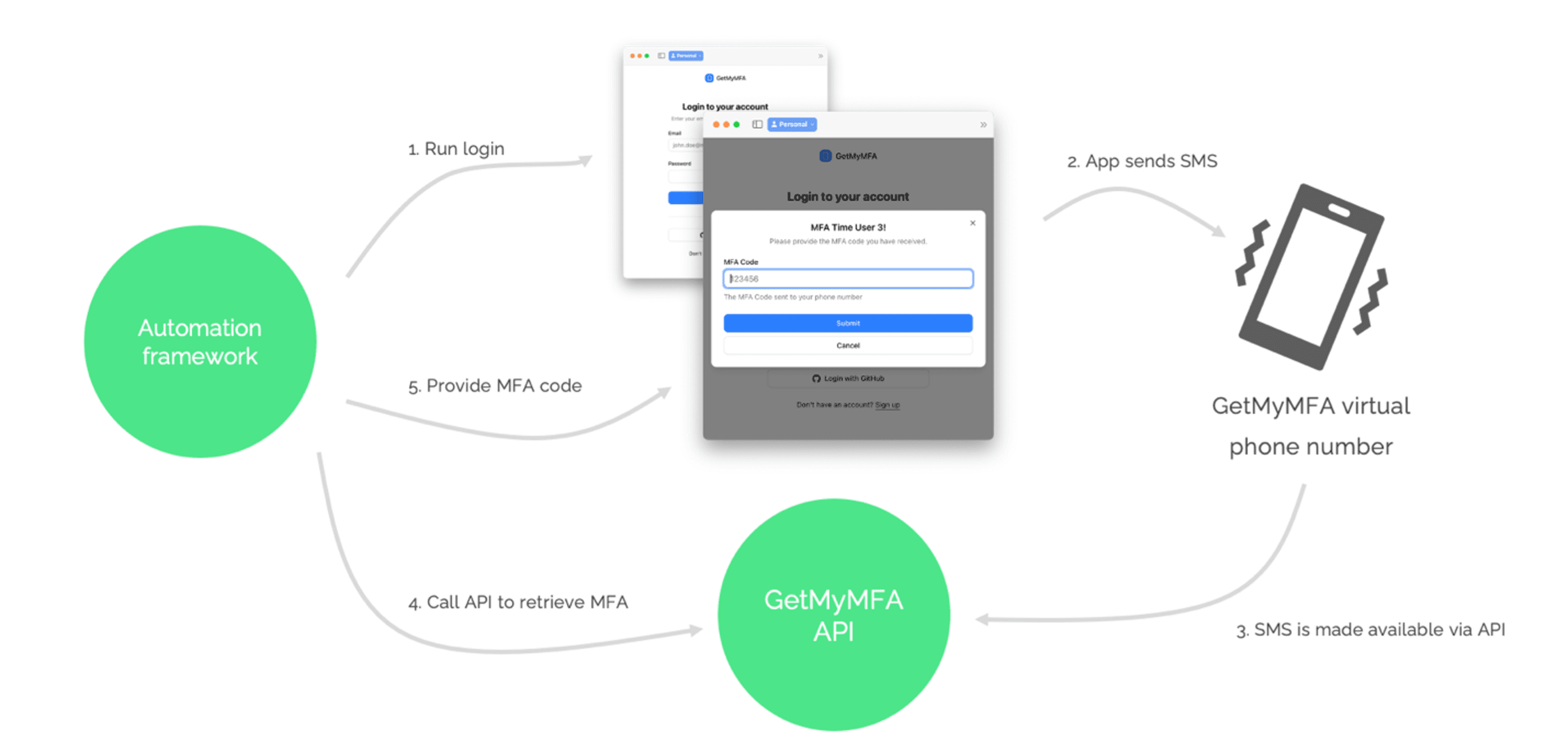
Note: In this demo, the actual SMS send (step 2) is skipped to avoid cost; the rest remains fully automated.
Tutorial: Set up Cypress + GetMyMFA
Step 1 — Install Cypress
If you already have a project, install Cypress as a dev dependency:
npm install cypress --save-devThen open Cypress for the first time to generate the default folder structure:
npx cypress openSelect E2E Testing in the welcome screen, pick a browser, and Cypress will scaffold the following folders:
my-project/
├── cypress/
│ ├── e2e/ ← your test files go here
│ ├── fixtures/ ← static test data
│ └── support/
│ ├── commands.ts ← custom commands (we will add one)
│ └── e2e.ts ← runs before every spec
├── cypress.config.ts ← project configuration
└── package.jsonIf you are starting from scratch, create a new folder and run npm init -y first, then install Cypress.
You will also need dotenv to load environment variables:
npm install dotenv --save-devStep 2 — Create a GetMyMFA test account + API key
Head to get.mymfa.io and click Sign Up. The Trial plan gives you a temporary virtual phone number with full API access.
Once signed in, go to API Configuration and create an API key. Copy it somewhere safe — you will need it in the next steps.
Step 3 — Get your virtual phone number ID
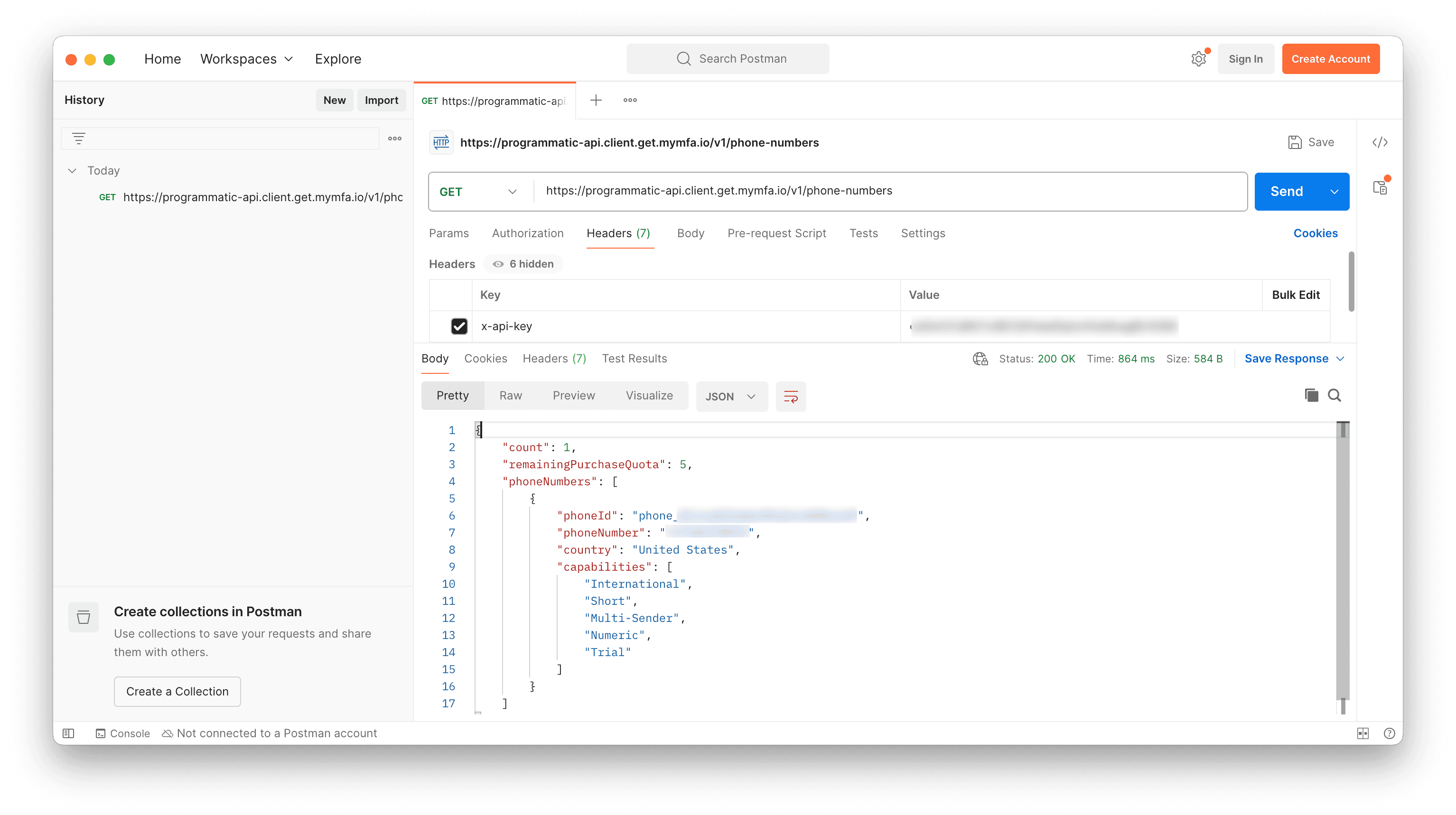
Using your API key as an x-api-key header, call the following endpoint:
GET https://programmatic-api.client.get.mymfa.io/v1/phone-numbersThe response includes a phoneId field. Save this value — your test will use it to retrieve MFA codes. You can also verify everything works by calling:
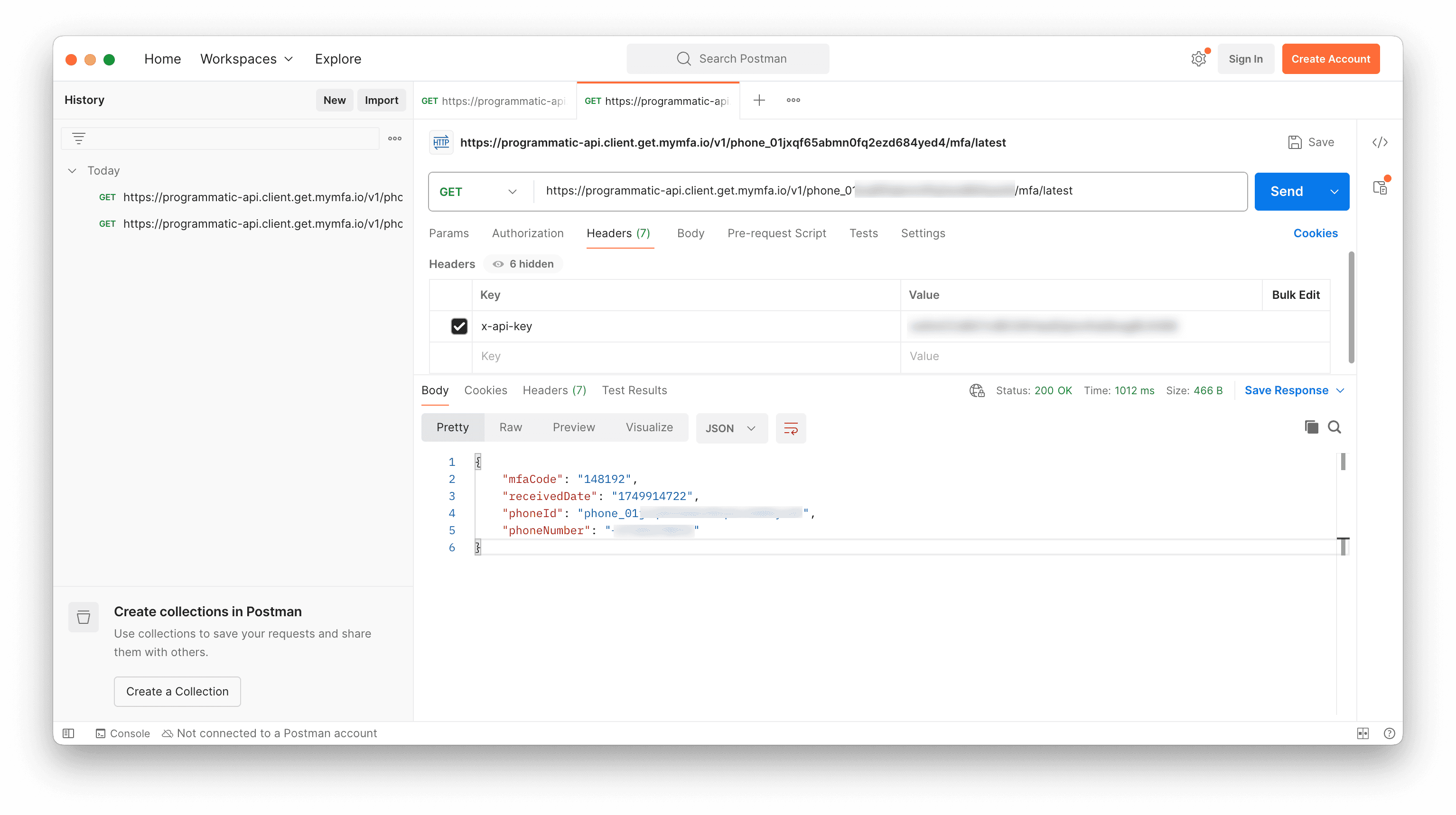
GET https://programmatic-api.client.get.mymfa.io/v1/<YOUR_PHONE_ID>/mfa/latestThe code is in the mfaCode field of the response.
Here is what the second call looks like when you fetch the latest MFA code:
Step 4 — Configure environment variables
Create a .env file in the root of your project with your credentials:
GETMYMFA_PHONE_NUMBER_ID=your_phone_id_here
GETMYMFA_API_KEY=your_api_key_here
TEST_USER_EMAIL=your_test_email
TEST_USER_PASSWORD=your_test_passwordThen update your cypress.config.ts to load them into the Cypress environment:
import { defineConfig } from 'cypress'
import * as dotenv from 'dotenv'
dotenv.config()
export default defineConfig({
e2e: {
baseUrl: 'https://demo.mymfa.io',
setupNodeEvents(on, config) {
config.env = {
...config.env,
GETMYMFA_PHONE_NUMBER_ID: process.env.GETMYMFA_PHONE_NUMBER_ID,
GETMYMFA_API_KEY: process.env.GETMYMFA_API_KEY,
TEST_USER_EMAIL: process.env.TEST_USER_EMAIL,
TEST_USER_PASSWORD: process.env.TEST_USER_PASSWORD,
}
return config
},
},
})This approach keeps secrets out of your code. The setupNodeEvents function runs in Node.js (not the browser), so it can safely read process.env values and inject them into Cypress.env().
Make sure.envis listed in your.gitignoreso you never commit secrets to version control.
Step 5 — Add a custom command to fetch the MFA code
Cypress has a powerful feature called custom commands that lets you encapsulate reusable logic. We will create a getMfaCode command that calls the GetMyMFA API using cy.request():
// cypress/support/commands.ts
Cypress.Commands.add('getMfaCode', () => {
const phoneId = Cypress.env('GETMYMFA_PHONE_NUMBER_ID')
const apiKey = Cypress.env('GETMYMFA_API_KEY')
return cy.request({
method: 'GET',
url: `https://programmatic-api.client.get.mymfa.io/v1/${phoneId}/mfa/latest`,
headers: {
'x-api-key': apiKey,
'Content-Type': 'application/json',
},
}).then((response) => {
return response.body.mfaCode
})
})cy.request() is Cypress's built-in way to make HTTP calls. Unlike fetch or axios, it is fully integrated into the Cypress command chain, which means it automatically waits, retries, and logs in the Cypress test runner.
If you are using TypeScript, add a type declaration so your editor recognizes the new command:
// cypress/support/index.d.ts
declare namespace Cypress {
interface Chainable {
getMfaCode(): Chainable<string>
}
}Step 6 — Write the E2E test
Create a new file at cypress/e2e/mfa-login.cy.ts with the following test:
describe('Login with SMS-based MFA', () => {
it('completes the full MFA login flow', () => {
// Navigate to the demo login page
cy.visit('/login')
cy.title().should('include', 'GetMyMFA')
// Fill in login fields and start sign-in
cy.get('[name="email"]').type(Cypress.env('TEST_USER_EMAIL'))
cy.get('[name="password"]').type(Cypress.env('TEST_USER_PASSWORD'))
cy.contains('button', 'Login').click()
// Ensure MFA prompt is visible
cy.contains('MFA Time').should('be.visible')
// Fetch MFA code via GetMyMFA API and submit it
cy.getMfaCode().then((mfaCode) => {
cy.get('[name="mfaCode"]').type(mfaCode)
cy.contains('button', 'Submit').click()
})
// Confirm login succeeded
cy.contains('MFA code verified').should('be.visible')
})
})Let us walk through what this test does:
cy.visit('/login')— Opens the login page. The base URL is defined incypress.config.ts, so you only need the path.cy.get()+.type()— Finds the email and password fields by theirnameattribute and types the credentials.cy.contains('button', 'Login').click()— Clicks the Login button.cy.contains()finds an element by its text content, scoped to buttons.cy.getMfaCode()— Calls our custom command, which hits the GetMyMFA API and returns the code..then((mfaCode) => ...)— Once we have the code, we type it into the MFA field and submit.cy.contains('MFA code verified')— Asserts that the login succeeded.
Run your test with:
npx cypress run --spec cypress/e2e/mfa-login.cy.tsOr open the Cypress UI to watch it execute step by step:
npx cypress openBest Practices for MFA Test Automation
Security Considerations
- Environment Isolation: Use dedicated test environments with separate MFA configurations. Never use production phone numbers in tests.
- API Key Management: Store API keys as environment variables or CI/CD secrets, never hard-coded in your test files.
Test Reliability
- Stable Selectors: Use
data-testidattributes ornameattributes rather than CSS classes that may change. Cypress also supports best practices for selecting elements. - Retry Logic: If the MFA code is not immediately available (e.g., SMS delivery delay), add a small
cy.wait()before calling the API, or implement a retry loop withcy.request()checks.
CI/CD Integration
- Headless Mode: Run
npx cypress runin CI — Cypress runs headless by default in this mode. - Parallel Execution: Use unique virtual numbers for parallel test runs to avoid MFA code collisions between tests.
- Environment Variables: Configure API credentials through your CI provider's secret management (GitHub Actions secrets, GitLab CI variables, etc.).
- Artifacts: Cypress automatically captures screenshots on failure and can record videos of test runs — enable these in CI for debugging.
Final thoughts
Automating MFA testing with Cypress does not require complex workarounds. With the GetMyMFA API and a simple custom command, your tests can handle SMS-based verification codes just like any other form field.
The result is an end-to-end test that mirrors real user behavior, without disabling security features or resorting to manual steps. This gives your team confidence that authentication works correctly before every deployment.
Whether you are running tests locally or in a CI pipeline, this pattern scales cleanly. Set it up once, and every test run validates your MFA flow automatically.
Ready to automate your MFA testing?
Start with a free trial • No credit card required • Full API access
